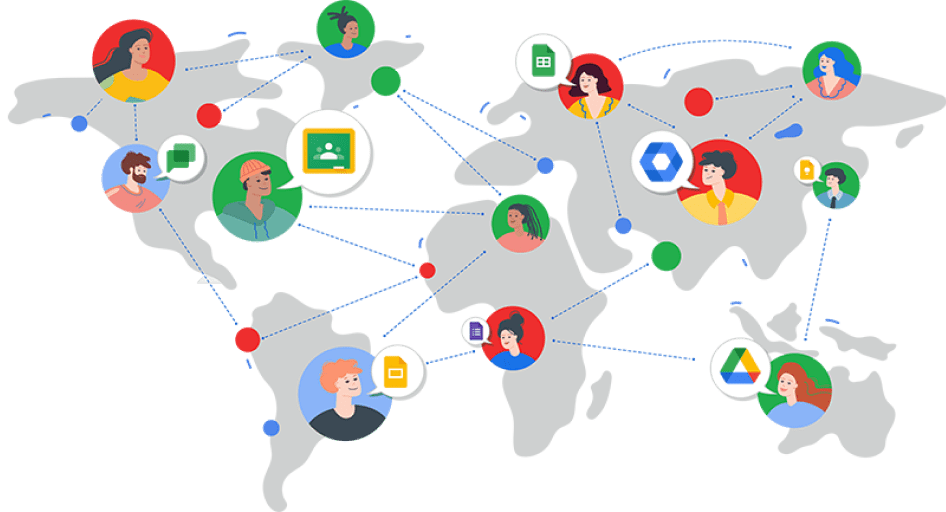
Empieza de la mano de tu Partner
uCloud es el partner y colaborador especializado en Google a nivel global, ofreciendo todo
nuestro expertise y conocimiento, acompañado de servicios, para una implementación ágil de
las soluciones Google.
Cada año seguimos creciendo más
a nivel Global
Algunos de nuestros clientes al lo largo de los años











+1000
Clientes
+60
Certificaciones
100%
Focus Google
5
Continentes
Deja que Google y nuestra experiencia en el sector te ayude
a impulsar tu empresa
Todos los productos y servicios
de Google a un click

Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google Cloud Platform es la infraestructura de Google en la nube, que cuenta con una amplia gamma de servicios avanzados, como IaaS, PaaS o SaaS.

Dispositivos Chrome OS
Amplia gama de dispositivos Google basados en la nube y el trabajo colaborativo. El uso de los dispositivos Chrome (Chrome OS) te supondrán un gran cambio en tu día a día en el trabajo.

Google Workspace
Google Workspace es el entorno colaborativo en la nube de Google diseñado para mejorar la eficiencia, colaboración y seguridad en el trabajo, estés dónde estés.